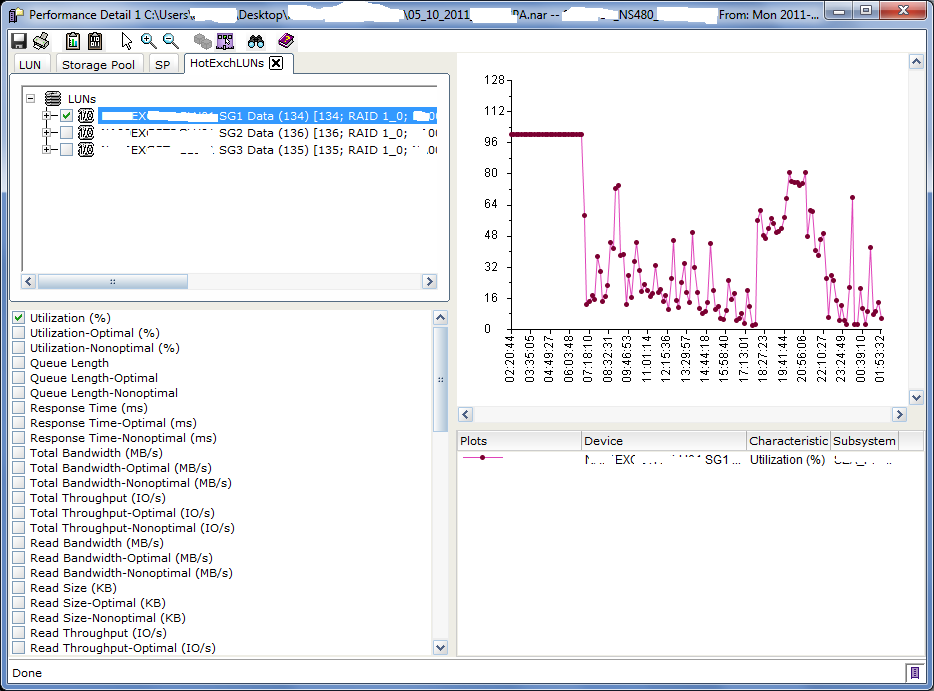
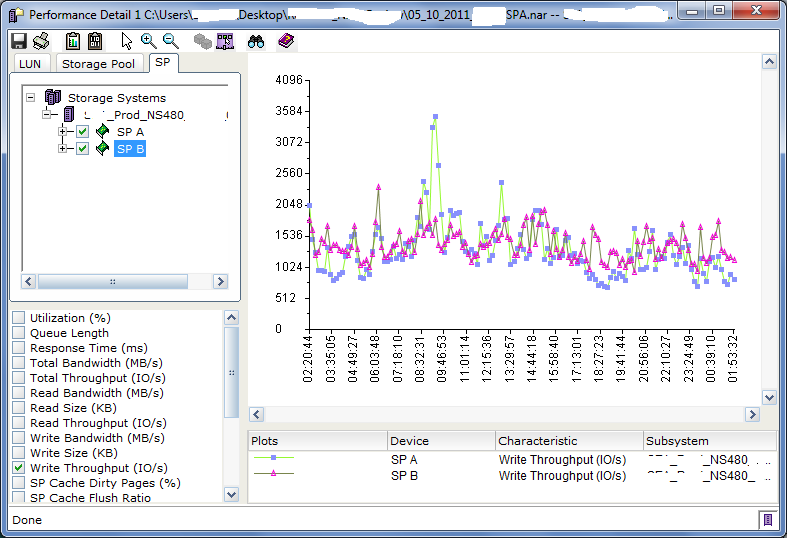
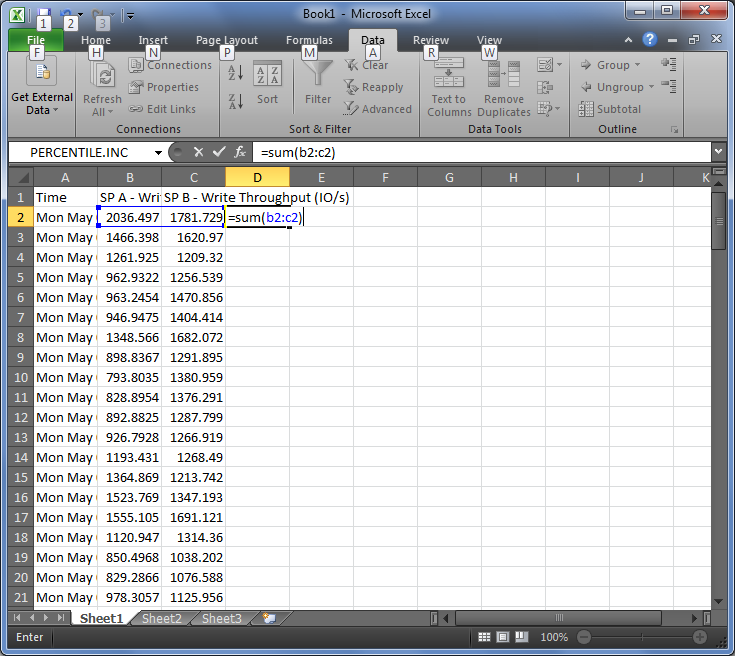
Do you have a clearly defined Recovery Point Objective (RPO) for your data? What about a clearly defined Recovery Time Objective (RTO)?
One challenge I run in to quite often is that, while most customers assume they need to protect their data in some way, they don’t have clear cut RPO and RTO requirements, nor do they have a realistic budget for deploying backup and/or other data protection solutions. This makes it difficult to choose the appropriate solution for their specific environment. Answering the above questions will help you choose a solution that is the most cost effective and technically appropriate for your business.
But how do you answer these questions?
First, let’s discuss WHY you back up… The purpose of a backup is to guarantee your ability to restore data at some point in the future, in response to some event. The event could be inadvertent deletion, virus infection, corruption, physical device failure, fire, or natural disaster. So the key to any data protection solution is the ability to restore data if/when you decide it is necessary. This ability to restore is dependent on a variety of factors, ranging from the reliability of the backup process, to the method used to store the backups, to the media and location of the backup data itself. What I find interesting is that many customers do not focus on the ability to restore data; they merely focus on the daily pains of just getting it backed up. Restore is key! If you never intend to restore data, why would you back it up in the first place?
What is the Risk?
USA Today published an article in 2006 titled “Lost Digital Data Cost Businesses Billions” referencing a whole host of surveys and reports showing the frequency and cost to businesses who experience data loss.
Two key statistics in the article stand out.
- 69% of business people lost data due to accidental deletion, disk or system failure, viruses, fire or another disaster
- 40% Lost data two or more times in the last year
Flipped around, you have at least a 40% chance of having to restore some or all of your data each year. Unfortunately, you won’t know ahead of time what portion of data will be lost. What if you can’t successfully restore that data?
This is why one of my coworkers refuses to talk to customers about “Backup Solutions”, instead calling them “Restore Solutions”, a term I have adopted as well. The key to evaluating Restore Solutions is to match your RPO and RTO requirements against the solution’s backup speed/frequency and restore speed respectively.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
Since RPO represents the amount of data that will be lost in the event a restore is required, the RPO can be improved by running a backup job more often. The primary limiting factor is the amount of time a backup job takes to complete. If the job takes 4 hours then you could, at best, achieve a 4-hour RPO if you ran backup jobs all day. If you can double the throughput of a backup, then you could get the RPO down to 2 hours. In reality, CPU, Network, and Disk performance of the production system can (and usually is) affected by backup jobs so it may not be desirable to run backups 24 hours a day. Some solutions can protect data continuously without running a scheduled job at all.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
Since RTO represents the amount of time it takes to restore the application once a recovery operation begins, reducing the RTO can be achieved by shortening the time to begin the restore process, and speeding up the restore process itself. Starting the restore process earlier requires the backup data to be located closer to the production location. A tape located in the tape library, versus in a vault, versus at a remote location, for example affects this time. Disk is technically closer than tape since there is no requirement to mount the tape and fast forward it to find the data. The speed of the process itself is dependent on the backup/restore technology, network bandwidth, type of media the backup was stored on, and other factors. Improving the performance of a restore job can be done one of two ways – increase network bandwidth or decrease the amount of data that must be moved across the network for the restore.
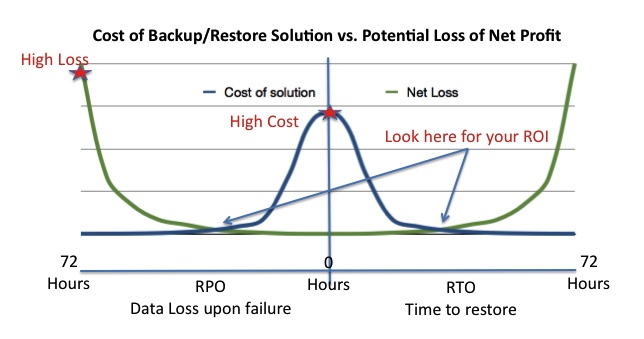
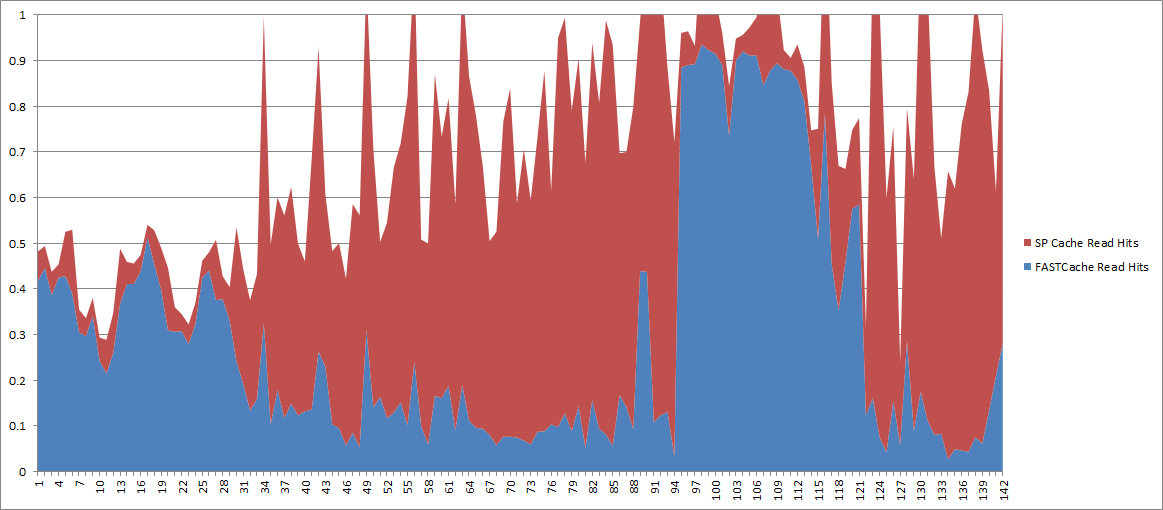
This simple graph shows the relationship of RTO and RPO to the cost of the solution as well as the potential loss. The values here are all relative since every environment has a unique profit situation and the myriad backup/restore options on the market cover every possible budget.
The values here are all relative since every environment has a unique profit situation and the myriad backup/restore options on the market cover every possible budget.
Improving RTO and/or RPO generally increases the cost of a solution. This is why you need to define the minimum RPO and RTO requirements for your data up front, and why you need to know the value of your data before you can do that. So how do you determine the value?
Start by answering two questions…
How much is the data itself worth?
If your business buys or creates copyrighted content and sells that content, then the content itself has value. Understanding the value of that data to your business will help you define how much you are willing to spent to ensure that data is protected in the event of corruption, deletion, fire, etc. This can also help determine what Recovery Point Objective you need for this data, ie: how much of the data can you lose in the event of a failure.
If the total value of your content is $1000 and you generate $1 of new content per day, it might be worth spending 10% of the total value ($100) to protect the data and achieve an RPO of 24 hours. Remember, this 10% investment is essentially an insurance policy against the 40% chance of data loss mentioned above which could involve some or all of your $1000 worth of content. Also keep in mind that you will lose up to 24 hours of the most recent data ($1 value) since your RPO is 24 hours. You could implement a more advanced solution that shortens the RPO to 1 hour or even zero, but if the additional cost of that solution is more than the value of the data it protects, it might not be worth doing. Legal, Financial, and/or Government regulations can add a cost to data loss through fines which should also be considered. If the loss of 24 hours of data opens you up to $100 in fines, then it makes sense to spend money to prevent that situation.
How much value does the data create per minute/hour/day?
Whether or not your data itself has value on it’s own, the ability to access it may have value. For example, If your business sells products or services through a website and a database must be online for sales transactions to occur, then an outage of that database causes loss of revenue. Understanding this will help you define a Recovery Time Objective, ie: for how long is it acceptable for this database to be down in the event of a failure, and how much should you spend trying to shorten the RTO before you get diminishing returns.
If you have a website that supports company net profits of $1000 a day, it’s pretty easy to put together an ROI for a backup solution that can restore the website back into operation quickly. In this example, every hour you save in the restore process prevents $42 of net loss. Compare the cost of improving restore times against the net loss per hour of outage. There is a crossover point which will provide a good return on your investment.
Your vendor will be happy when you give them specific RPO and RTO requirements.
Nothing derails a backup/recovery solution discussion quicker than a lack of requirements. Your vendor of choice will most likely be happy to help you define them but it will help immensely if you have some idea of your own before discussions start. There are many different data protection solutions on the market and each has it’s own unique characteristics that can provide a range of RPO and RTO’s as well as fit different budgets. Several vendors, including EMC, have multiple solutions of their own — one size definitely does not fit all. Once you understand the value of your data, you can work with your vendor(s) to come up with a solution that meets your desired RPO and RTO while also keeping a close eye on the financial value of the solution.
Like this:
Like Loading...