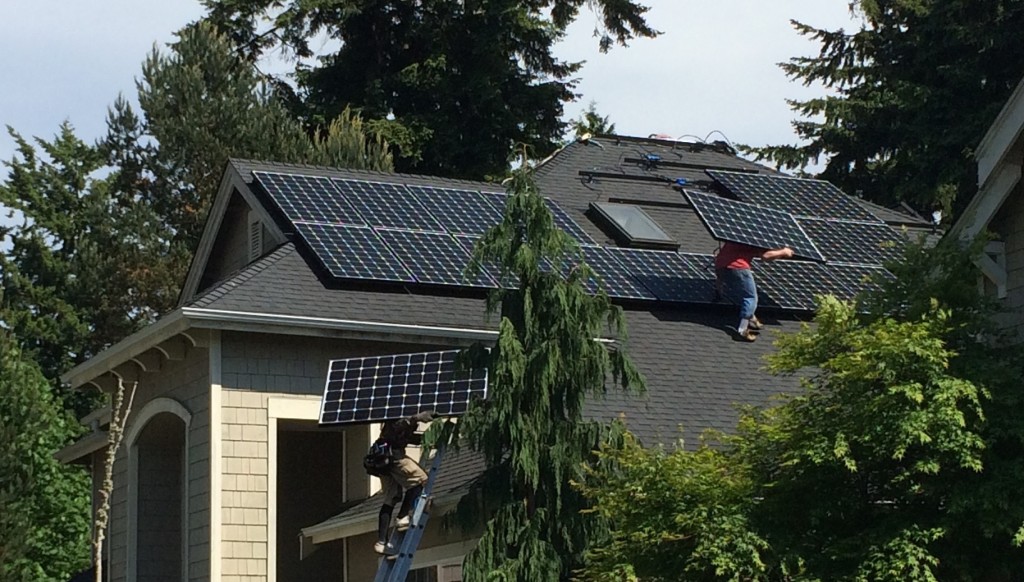
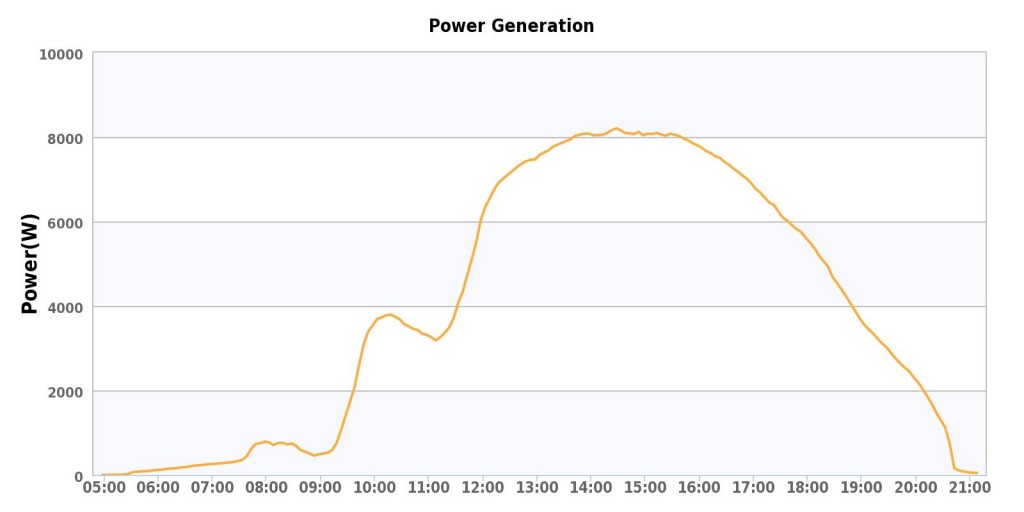
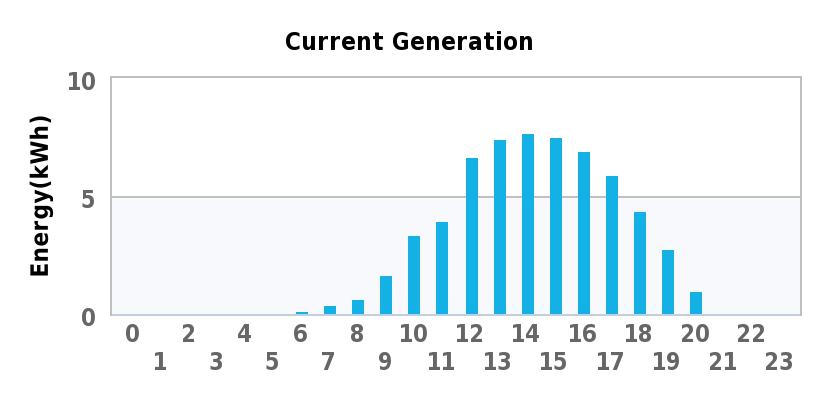
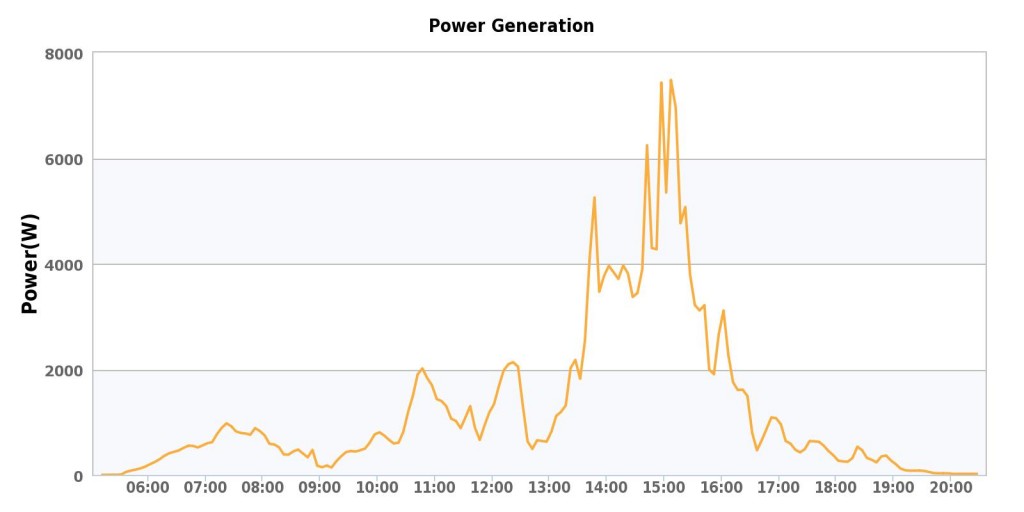
Well, it’s been just over a month since the solar system came online..
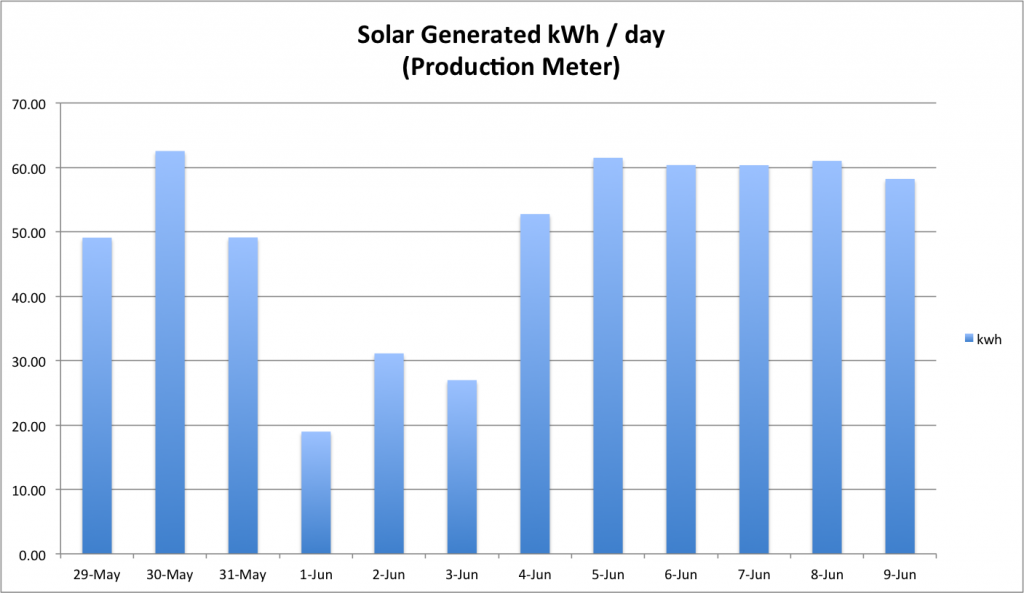
In the 33 days that the solar system has been online, we’ve generated a total of 1817kWh from the panels.. Due to line losses and differences in measurement intervals and such the PSE Production meter has registered 1724kWh.
- For the Washington State REAP program that we are participating in, that 1724kWh translates to ~$930 in state incentives generated so far.
The PSE Net meter which is what our monthly power bill is based on has two useful values..
- First, we’ve pushed a total of 1205kWh of excess solar power to the grid. This means that from the solar power itself, during the day, we’ve consumed 519kWh that came straight from the solar panels and didn’t have to be pulled from the grid.
- On a more grand scale, the full 1205kWh is power that didn’t have to be generated somewhere by a Nuclear, Gas, Coal, etc power plant. What happens if you scale that up to more homes?
- Second, we pulled a total of 602kWh during the same period, primarily at night when the solar panels are not generating any power.
- Now, what if the excess we pushed into the grid above was stored at the power company’s neighborhood substation in a bank of batteries (Tesla Energy?) and then this power that we pulled at night came from those batteries. Suddenly the power generation get’s much simpler and demand spikes are smoothed out… But I digress.
So our total consumption of power during the 33 days was about 1121kWh, and we generated 1724kWh. Due to how net metering works, our electric bill will now have a credit equal to 602kWh. Unfortunately, because the power company fiscal year is July through June, this credit is more or less a throw-away.. It get’s zeroed out at the end of June. But going forward from July until June 2016, as we generate more credit we will be able to consume that credit during the winter months as needed to cover the difference between what we generate and what we consume.
Oh, it’s freakin’ HOT here right now compared to normal, and we have no AC, so the furnace fan and about four other fans are all running pretty much non-stop. This combined with charging our electric car (actually a very small amount of power) is pushing our power consumption up a bit higher than normal. Typically we consume about 100kWh more in August than in other months due to running the fans, but we’ve had a very warm spring, today (July 1st) it’s 92F here and the average is only 73F. The record for this day, prior to today was only 84F.
At $0.10/kWh, we would have paid about $100 for electricity. But instead the power we pushed to the grid has more than offset that and our bill will essentially be ~$7 for the base connectivity charge.
You can browse around my online solar reports if you want – StorageSavvy’s Solar Dashboard